Micro Injection Molding
Micro injection molding is an advanced manufacturing process that involves the shaping of extremely small, high-precision plastic components with complex geometries. It stands as a cornerstone in modern manufacturing realms where miniaturization and precision are paramount. This technique leverages specialized machines capable of delivering material into molds with tight tolerances at micro levels, paving the way for advancements across various industries including medical devices, electronics, and aerospace engineering. The significance of this technology lies in its ability to mass-produce intricate parts with consistent quality and functional properties that conventional molding methods cannot achieve, thus revolutionizing the production landscape of small-scale components.
Principles of Micro Injection Molding
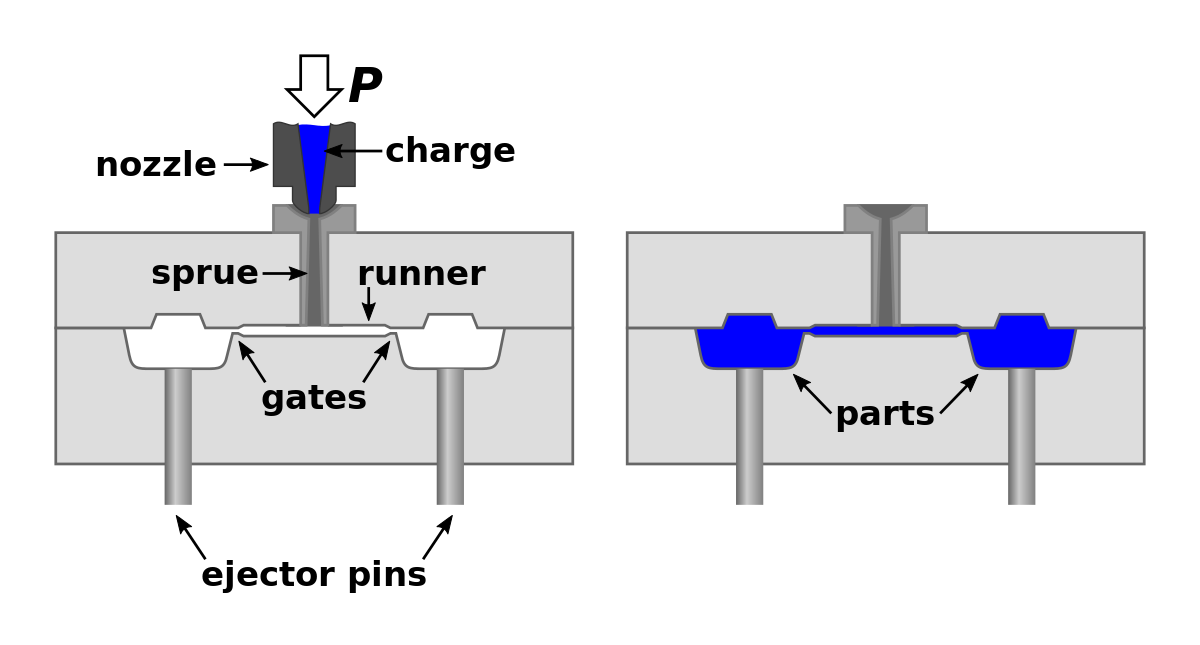
The micro injection molding process operates on the principles similar to conventional injection molding but with a focus on miniaturization and precision. At its core, the process involves injecting molten thermoplastic material into a mold where it solidifies into a predefined shape. A key component is the micro-injection unit, which must perform with high accuracy due to the small shot sizes and intricate mold cavities involved. The plasticizing unit plays an essential role in precisely melting and homogenizing the polymer before injection. Another crucial element is the mold itself which must be manufactured with exceptional precision to produce the tiny features characteristic of micro molded parts. Additionally, specialized controllers are implemented to manage the complex parameters required for consistency in micro-scale production runs. These include precise temperature control, injection speed, and pressure systems that guarantee the integrity of delicate components.
Benefits of Micro Injection Molding
The benefits of micro injection molding are manifold, particularly when it comes to the precision and capability it offers for manufacturing small components. Its advanced technology allows the creation of minute parts with complex features that are too delicate for traditional molding methods. Another notable advantage is material efficiency; this process uses less raw material and substantially reduces waste, making it a more sustainable option. Additionally, micro injection molding lends itself to enhanced production speeds, which is key for high volume runs where time and consistency are critical factors. With this method, manufacturers enjoy superior part quality and consistent replication of parts, ensuring reliability in applications where deviations can be costly or dangerous.
Applications of Micro Injection Molding
Micro injection molding has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape with its precision and efficiency, finding a stronghold across diverse industries. In the medical field, it facilitates the production of intricate devices and surgical tools that require exact specifications for patient safety and performance. Similarly, in electronics, this technology is essential for creating micro-electronic components and connectors which demand high precision to ensure reliable functionality in compact spaces. The automotive sector also benefits greatly from micro injection molding; it is utilized to fabricate small, complex parts that contribute to the overall performance and weight reduction in vehicles. A pertinent case study is the development of micro-sized plastic gears used in minimally invasive surgical robots, showcasing how micro injection molding enables the integration of minute yet robust components into sophisticated apparatus.
Comparison to Traditional Injection Molding
Differentiating factors between micro injection molding and traditional injection molding are pronounced, given their distinct capabilities. Micro injection molding specializes in producing extremely small, high-precision components with a weight of less than one gram and features that reach the micrometer scale. This is feasible due to specialized machines that hold tighter tolerances and have finer control over injection pressure and speed. In contrast, traditional injection molding is suited for larger parts and typically struggles with the precision required for miniature components. The decision to use micro or traditional methods hinges on various factors such as part size, detail complexity, material selection, and production volume. Manufacturers may opt for micro molding when fabricating intricate medical devices, microelectronics, or micro-optics, where immaculate detail and accuracy are non-negotiables. Conversely, traditional injection molding is more cost-effective and time-efficient for bulk manufacturing of larger items like automotive components or consumer product casings.
Future of Micro Injection Molding
The future of micro injection molding is poised to be revolutionized by continuous technological advancements and innovations. As manufacturers increasingly prioritize precision, energy efficiency, and waste reduction, new methods such as 3D printing for micromold fabrication and machine learning for process optimization are set to refine the capabilities of micro injection molding equipment. The shift towards micro-scale production is anticipated in various industries, from medical devices, where minute components are crucial, to electronics that continually demand smaller, high-performance parts. These industry shifts may drive further research into materials compatible with micro injection molding and advancement in tooling technologies to achieve greater accuracy and repeatability in mass-produced micron-sized products.
Materials and Sustainability in Micro Injection Molding
Micro injection molding uses a variety of materials, including thermoplastics, elastomers, and some metals. These materials are chosen based on their properties that suit the intricate nature of micro-sized components. The process contributes to sustainability by minimizing waste material and enabling the production of lightweight parts which reduce overall energy consumption when used in applications such as aerospace or automotive industries. For mass production, micro injection molding is highly efficient; it can produce high volumes of parts with consistent quality and precision. Various industries, particularly medical, electronics, and consumer products, reap significant benefits from this technology due to the demand for small, complex parts. The unparalleled precision of micro injection molding directly impacts an end-product’s performance by ensuring tight tolerances and exacting specifications essential in miniaturized components.